Carter System
Well Explorer > Site Properties or Well Properties > Location Description Tab
The Carter coordinate system is a land grid, based on latitude and longitude, used to locate oil and gas well data typically in the states of Kentucky and Tennessee.

This system was originally developed by the Carter Oil Company to mimic the township and range location system in areas that had not been surveyed.
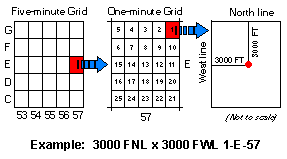
The Carter Coordinate system divides the state into quadrants of 5' latitude by 5' longitude. It then further subdivides each quadrant into 1' latitude by 1' longitude sections. The location of the well is then identified by it's distance from two adjacent boundaries of the 1' by 1' section.
In Kentucky, each of the 5' by 5' quadrants running east/west (townships) are labeled with letters ranging from A in the south to Z and then AA to GG in the north. The quadrants running north/south (ranges) are labeled with numbers ranging from 0 in the west to 92 in the east.
Each quadrant is subdivided into 25 1' latitude by 1' longitude sections. Within this subdivision the location of the well is specified by the distance from an adjacent pair of one-minute section boundaries to the well.
For example, a well located in quadrant township B and range 16, which lies 400 ft from the East line and 1050 ft from the South line boarder of the 1' by 1' section numbered 12 would be identified in the following way: 1050 FSL X 400 FEL 12-B-16
Source References:
University of Kentucky, "Kentucky Geological Survey, FAQ: What is the Carter coordinate system?", http://www.uky.edu/KGS/emsweb/kyogfaq/kyogfaq9.html (© 2002 Created 18-Jul-2002 Last modified 01/22/2003 16:04:14).